Market Turbulence Ahead
Market Turbulence Ahead
This is your captain speaking…
When you’re on a commercial flight, and the plane is approaching turbulence, the captain comes on the intercom to let you know to buckle up and expect ‘rough air.’ There should be similar warnings about ‘rough air’ in the markets, and this is a good time to offer one.
The market turbulence that we see approaching is a consequence of the debt ceiling debate—or, rather, the refusal of Congressional leaders to agree to raise the limit on the amount of bonds the government is allowed to sell to finance its operations. The legal limit on the amount of Treasury debt that the government can issue is periodically raised—and it is always because Congress has already authorized a budget that will exceed the debt limit.
Yes, you read that right. Congress created a gap between revenues collected and expenditures, and now is threatening not to authorize the payments that were approved. Don’t try this at home.
Of course, this is a political issue, as are all things in Washington. Republican leaders, who control the U.S. House of Representatives, believe that their colleagues on the other side of the aisle will be so appalled at the idea of the wealthiest nation on earth defaulting on its fiscal obligations to bondholders, Social Security recipients and government employees that they will be willing to negotiate Republican-proposed spending cuts, including reductions in federal health care, science and education. Among the few specific proposals is a rule requiring low-income Medicaid recipients to work for 80 hours a month, blockage of the proposed student debt cancellation, and a repeal of a variety of green energy initiatives. The most contentious proposal would scale back medical benefits for military veterans.
Ironically, the Democratic budget proposal would reduce the federal deficit, over the long-term, by $3 trillion. But instead of budget cuts, it would raise the highest corporate tax rate from 21% to 28% and impose a 25% minimum income tax on billionaires. The proposal would also raise the highest tax rate for couples earning more than $450,000 to 39.6%.
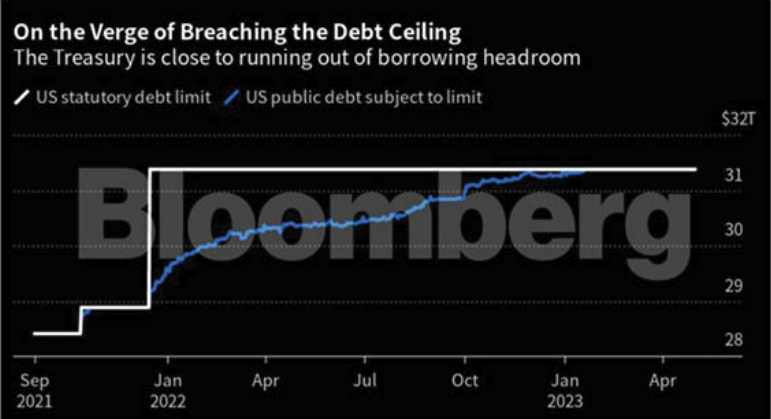
How likely is a default? The U.S. government actually hit its maximum debt ($31.38 trillion) on January 19, and has since been relying on accounting tricks like deferring pension investments in order to keep the doors open and the bond payment checks from bouncing. We are now on a near-approach to what insiders call the ‘x-date,’ the unspecified time when those measures will be insufficient, and the government will have to start deciding who to pay and (more to the point) who not to pay out of its diminishing resources. It’s worth pointing out that previous debt-ceiling brinkmanship caused credit agencies to lower America’s credit rating—once the highest in the world.
You can bet that quick-twitch traders, whose activities drive short-term market movements, are carefully watching this dance on the edge of default. If the government does run out of its ability to pay bond-holders and workers, those traders would most likely retreat to the sidelines, and there would be at least short-term panic among lay investors who would see sharp lurches in the value of their stock holdings. None of this would affect the actual value of shares of stock (or the value of public companies) in any way, but in the short-term, especially when there are screaming headlines of potential default and dire economic consequences, confidence (or lack thereof) trumps rationality every time.
You know that, sooner rather than later, both sides will come to an agreement that the U.S. should pay its obligations, and some semblance of normalcy will be restored. In the meantime, the captain is advising you to fasten your seat belts.
Game of Chicken
The idea that the U.S. government has to manage its finances like a household is patently ridiculous. You and I and the family down the street don’t have the power to impose a tax on our fellow citizens and corporations when our bills come due.
Unlike the government, if we tried to print money, we’d get arrested. Unlike us, the government takes on a number of societal obligations that benefit various citizen constituencies, including protecting us from outside military threats, maintaining our legal system, running our national parks, paying the salaries of our Congressional representatives and people like air traffic controllers, food safety inspectors, Treasury workers and 75,000 other federal employees, not to mention cutting the checks for retirement benefits like Social Security and Medicare.
When you and I take on debt, it doesn’t show up in the marketplace as Treasury bonds; that is, when we incur debt, we don’t create what have long been regarded as the most stable investment option for peoples’ investment portfolios. You and I don’t have the power to issue our own currency, much less have it be the currency that global trade relies on.
But there is one area where managing the government’s finances and managing a household’s finances are pretty much identical: we both need to pay our bills on time. If you and I were to refuse, no matter how tempting that may be when the invoices arrive, there are consequences, pretty much all of them bad. For us consumers, not paying our bills will result in an accumulation of interest payments on the credit cards, a reduction in our credit score, and possibly foreclosure on our home, car and other assets that we’ve accumulated over the years.
For the government, the consequences are broader. Among other things, the government won’t stop paying interest on the bonds in investment portfolios, and there is potentially a huge loss of confidence in the world community about the willingness of the richest country in the world to meet its financial obligations like an adult.
This is, of course, a discussion about the current debt ceiling debate in Congress, and about the fact that, unless the U.S. House of Representatives votes to raise the debt ceiling, the government will run out of cash to pay its various bills on or about June 7.
Unfortunately, the issue has become political; House Republicans are demanding that the government impose some spending cuts (not always clearly articulated) before they’re willing to give their permission for the government to issue more bonds, while the Democrats are arguing that the Republicans are holding the country hostage.
If you want to run with the household analogy, the debate can be seen as a family recklessly running up a lot of debt, and then refusing to pay its bills until all the family members have agreed to set a proper budget in the future. And predictably, the family members can’t agree.
There is no question that the U.S. owes a lot more money to its various creditors and bond investors than it ever has before, and there is obviously a huge difference in spending philosophy between the two political parties. The problem for the rest of us is that a government default would impose a lot of collateral damage: the value of Treasury bonds would almost certainly plummet, because many bondholders would be uncertain about how and when they would get paid. There would be a nervous tremor rippling through the stock market, which would cause a temporary decline in the share prices of the stocks we own. Interest rates would skyrocket, because lenders and investors would demand higher returns for the added risk of not getting paid. Stable assets would look suddenly less stable. And there’s no telling what would happen to the value of the dollar.
The Council of Economic Advisors has calculated that a protracted default would result in the loss of 8.3 million jobs in the U.S. economy, and reduce GDP by 6.1%—a recession the size of the Great Recession that most of us still regard as a painful memory.
The debt ceiling may become a moot point in a month or so; most investors seem to be expecting that, before June 7, the House of Representatives will decide that it’s more important to pay America’s bills than to score political points. But it should be noted that the cost to insure U.S. bonds from default—known as the credit-default swaps—is now higher than the cost of similar instruments insuring the government bonds of Greece, Mexico, and Brazil. This is another way of saying not everybody is confident that this game of chicken will end peacefully.
Never before has the government passed that X-date without finally raising or suspending the statutory limit on federal debt. But if that deadline were to pass without action, and the U.S. finds itself in a global crisis entirely of its own making, then all of us will need to buckle up for a lot of market and economic turbulence.
None of this takes away from the fact that there are some very real questions about how the U.S. budget should be organized going forward; the government ‘household’ probably does need to get its finances in better order. If you have a spare hour or two, you might consider making your own budget decisions, through an online portal that allows all of us to input our priorities and see how that impacts the deficit going forward. Go here: https://www.crfb.org/debtfixer, and create your own government ‘household’ budget. You might find that it’s harder than you realize, throw up your hands and tell the government that it’s okay after all to start printing more bonds.
Losing Value Slower
Buying a new car is not an investment; that shiny new vehicle that you just purchased plunges in value the minute you drive it off the lot—which is probably not what you hope will happen with your retirement portfolio. But some cars lose value less rapidly than others.
Take, for example, the Toyota Tundra. Kelly Blue Book’s latest release estimates that after five years of ownership and reasonable care, you will be able to sell your Toyota Tundra for 73.3% of what you paid for it. (Yes, calculating such a thing down to a decimal point is ridiculous, but that’s how the publication lists it.)
The next best cars, in terms of five-year resale value, are the Toyota Tacoma and the Tesla Model X, which will normally fetch about 66% of what you paid five years ago. The recent report breaks down the resale rankings by type of car: SUVs, autos, trucks, electric vehicles, and minivans. Among cars, the Chevrolet Corvette stands out, with a 65.3% estimated 5-year resale value, followed by the Honda Civic (62.5%). Less notable, surprisingly, is the Lexus LS, which will only retain 44% of its value upon a 5-year resale. The truck with the highest resale value, according to Kelly Blue Book, is the aforementioned Tundra, followed by the Tacoma, and in general trucks seem to hold their value better than cars.
There’s a lot more that goes into car buying than resale value, and in general, the more expensive cars and trucks seem to do a better job of holding their value. The value investor will take into account how much their new car will be worth if you decide to sell it down the (proverbial) road.
Sources
- Treasury Department
- ABC News
- KTSM News
- The Economist
- Reuters
- The Washington Post
- The Telegraph
- White House
- Council on Foreign Relations
- Yahoo News
- Advisor Perspectives
- Kelly Blue Book
Download a PDF version of this article below.
 Market Turbulence Ahead
Market Turbulence Ahead